Auto Loan Debt
Buying a car in today's economy comes tagged with so much auto loan debt. Nonetheless, that has been important as a tool for spreading out the cost over time, especially allowing more people to be able to afford vehicles. The right moves in handling auto loans demand being careful about different factors based on making informed decisions in the respect of your financial goals and situations.
What are Auto Loans?
Auto loans are tailored products in purchasing a vehicle. Essentially, one is able to borrow money from a lender and repay it in a given time usually of three to seven years. Such loans are secured with the vehicle in that in case the borrower fails to pay by the agreed terms, the lender takes back the vehicle.
Types of Auto Loans
1. Traditional Auto Loans: A traditional auto loan is offered by banks, credit unions, and online lenders, in which a lump sum amount of dollars is lent to a borrower who used it for the purchase of a vehicle. These types of loans carry fixed or variable interest rates and are repayable within a stipulated period.
2. Dealer Financing: Most dealers will provide financing by arrangement with banks in their network. While this might be convenient, dealer financing may charge a higher interest than when one borrows directly from a bank or credit union.
3. Lease Buyout Loans: Some would like to buy out the car they had on lease at the end of the contract period. A lease buyout loan is what helps the consumer finance the purchase of that very car.
Pros and Cons of Auto Loans
Pros:
Ownership: You will have full ownership of the vehicle after you've paid off the loan.
Flexibility: There are loads of lending institutions offering the best terms and conditions tailored to suit your pocket or financial condition.
Building Credit: Making timely payments on your auto loan will increase your credit score since it involves responsible behavior in borrowing.
Cons:
Interest Costs: Auto loans come expensive with interest costs, raising the price of a vehicle that one is to pay.
Depreciation: Depreciation of a vehicle occurs after some period due to its usage. You may owe more money to that vehicle than what it is worth at present according to today's market during the early part of the loan term.
Risk of Repossession: If one fails to repay the installments, the vehicle can be repossessed and will definitely affect your credit score and a loss economically.
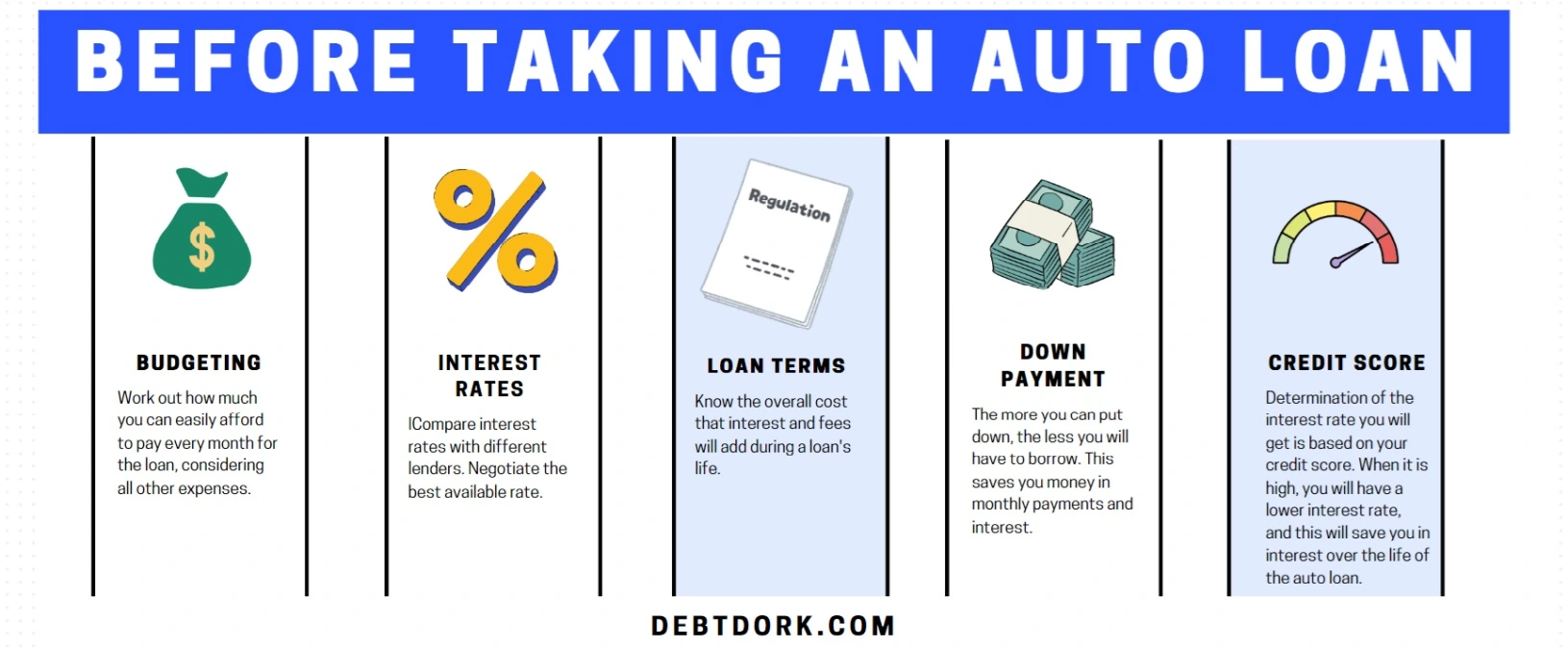
Things to Consider Before Taking an Auto Loan
1. Budgeting: Work out how much you can easily afford to pay every month for the loan, considering all other expenses.
2. Interest Rates: Compare interest rates with different lenders. Negotiate the best available rate.
3. Loan Terms: Know the overall cost that interest and fees will add during a loan's life.
4. Down Payment: The more you can put down, the less you will have to borrow. This saves you money in monthly payments and interest.
5. Credit Score: Determination of the interest rate you will get is based on your credit score. When it is high, you will have a lower interest rate, and this will save you in interest over the life of the auto loan.
Tips of Managing Auto Loan Debt
- Fine Print: Understand what the terms and conditions of the loan agreement are. These fine prints can include penalties for early repayment or late payment.
- Negotiate: Do not hesitate to negotiate regarding the interest rates or the fees for the loan in case you have a good credit history.
- Think Refinance: If interest rates have fallen or your credit score has improved significantly, it can be an opportune time for refinancing, seeking very affordable monthly payments with minimal interest costs rationale.
- Pay More When You Can: Large payments made towards the loan principal might shorten your life of the loan and lower the total amount payable in the form of interest.
Comparison: Auto Loan vs. Lease
Auto Loan:
• You Own It: You have ownership of your car once you've paid off the loan. • Cost: It requires higher monthly payments compared with a lease, but you will start building equity in your vehicle.
• Flexibility: You can customize with wild abandon and drive it as many miles as you want without additional fees.
Lease:
- Lower Payments: The amount of lease payment per month is normally less compared to that of the loan, since you're essentially covering the car's depreciation.
- Newer Cars: One gets the advantage of using a new car once in a few years, without worrying about the hassles of long-term car maintenance.
- Restrictions: Leases are associated with mileage restrictions and require, at the end of the lease, a person to return the vehicle to the lessor in good condition.
How to Choose Between an Auto Loan and a Lease :
Think Use: If you drive a lot or are into long-term owning, an auto loan is more suitable for you. To users who may have a love for driving newer cars and would like to pay less each month, leasing might just suit them fine.
Financial Implications: An auto loan will help in having equity in vehicle ownership and maybe improve credit scores. Leases provide reduced upfront costs with predictable expenses but no ownership benefits.
Additional Online Resources
1. Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB): Consumer guides and tools on auto loans. cfpb.gov
2. Edmunds: Detailed guides and calculators on all auto loan and leasing options. edmunds.com
3. Bankrate: Comparisons for auto loan rates with corresponding loan repayment estimators. bankrate.com
Auto loans make vehicle ownership quite assessable for very many people. Being conversant with the loan types available and weighting these against what your current financial situation puts one in a better position to make informed decisions that alignfully with long-term goals. Be it an auto loan or lease, the costs, terms, and conditions should be well taken into consideration to begin a financial responsibility mode while acquiring and financing your car.